Non-Destructive Testing Services
NDT helps ensure parts meet a quality standard before reaching market.
IPC Foundry Group offers non-destructive testing services for its cast components, including penetrant testing (PT), radiography/x-ray testing, magnetic testing (MT), and visual testing (VT) methods. In this article, we'll take a 101-style look at NDT, including the basics, methodologies, and how it can benefit your business. If you're interested in our NDT services or any of our other compliance offerings (heat treating, plating, solidification modeling, tooling repair, etc.), contact our team today. For more about non-destructive testing, read on!
What is Non-Destructive Testing?
Within the lens of investment casting, Non-destructive testing (NDT) is an inspection method that examines and tests metal components for quality and accuracy without causing damage to them. NDT enables parts that pass inspection to be released for market or field use, rather than being scrapped during the QC process.
Methods of NDT
At IPC, we use four different methods of NDT. Let's briefly explain each one.
PT (Penetrant Testing/ Liquid Penetrant Testing):
PT is a testing method that helps discover defects on or near the surface of a casting, including cracks or porosity points that are undetectable by visual inspection. Parts undergoing testing are cleaned, and then a special dye is applied to the surface of each component. After some time settling, this dye will penetrate any cracks or pores. Next, a developing agent is applied to the part, which pulls the penetrating dye back out, highlighting any defects or surface cracks.
Because PT is used to detect surface (or near-surface) level defects, it is frequently used in tandem with other testing methods, such as radiography, allowing for comprehensive part testing.
Magnetic Testing (MT)
In foundry work, MT is often used for ferrous castings as a quick method for confirming part integrity, especially for safety-critical applications. Tested castings are magnetized with an electric current, and then small magnetic particles are applied to the part. If there are defects at or near the part surface, particles will gather around these imperfections, highlighting them for QC personnel.
Much like PT, magnetic testing discovers defects at or near the surface of the part, such as cracks, pores, seams, and inclusions. It is beneficial for testing complex shapes and is quite cost-effective. However, MT doesn't work for non-magnetic materials such as aluminum or copper.
Visual Testing (VT)
As the name suggests, inspectors will use the naked eye or simple visual tools (magnifiers, cameras, mirrors, etc.) to examine the part for damage or defects. VT is often the first method applied, because many defects can be identified and sorted without the need for more advanced testing methods.
Of note, VT is frequently used throughout production to prevent failures; this can include things like inspecting wax patterns or shells before metal is even poured.
X-Ray Testing (Radiography):
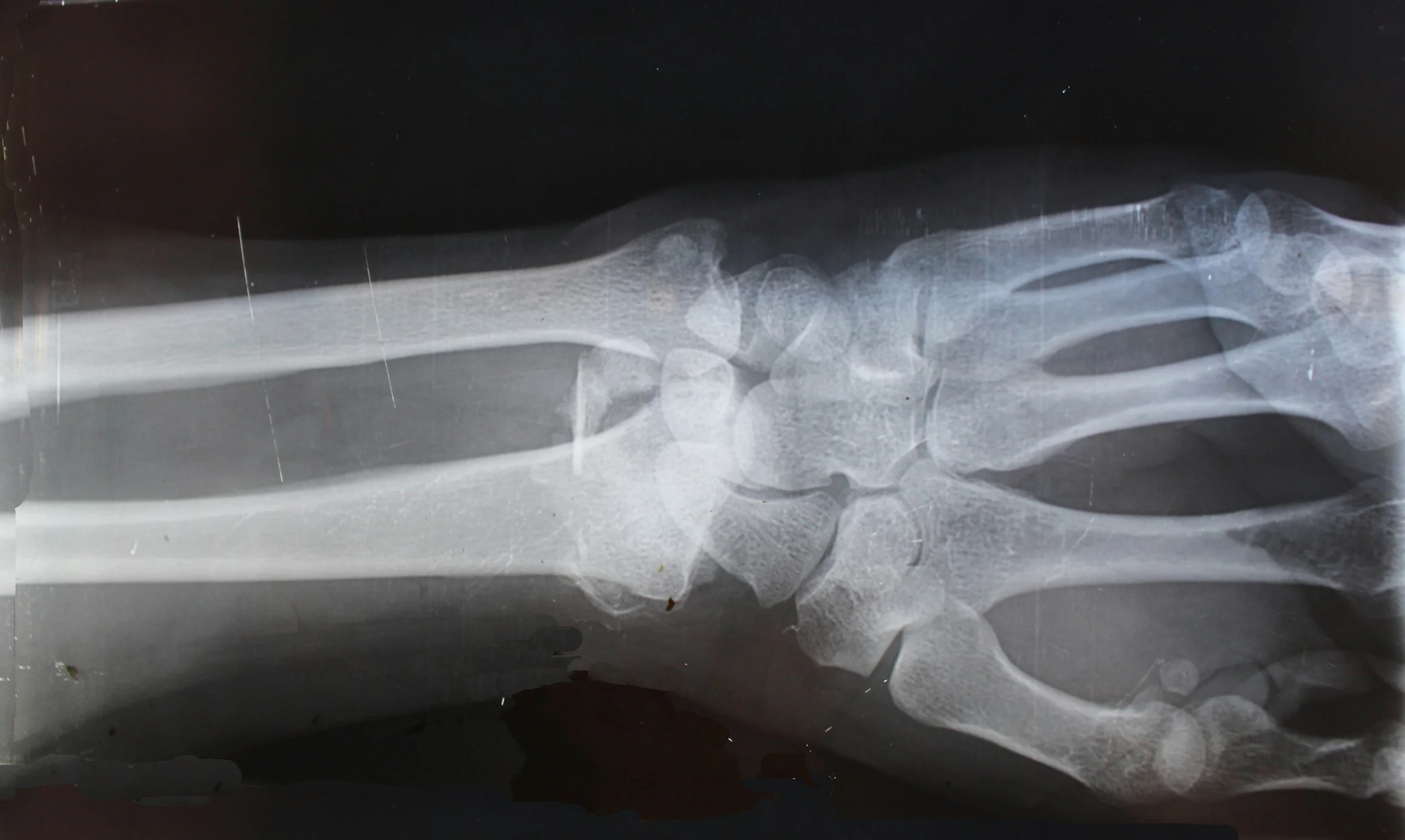
Similar to getting an X-ray at the doctor to check for a broken bone, testing personnel will use X-rays or Gamma rays to test for internal defects within castings. Faults can include cracks, inclusions, porosity, cavities, and other failures. In investment casting and foundry work, radiography is one of the most valuable NDT tools because it can confirm the internal soundness of a casting, ensuring there are no hidden issues that could cause failures in service.
X-ray testing is more expensive and time-consuming than other NDT methods. However, it can be an essential testing method for critical components such as castings used in aerospace or power generation.
You can think of Radiograph NDT much like an X-ray at the doctor
Why Use NDT?
1. Ensures Part Quality
NDT confirms that parts meet specifications and are free of critical defects before being shipped to customers or used in the field.
2. Prevents Failures in Service
By catching cracks, porosity, or hidden flaws early, NDT helps avoid costly breakdowns, safety risks, or recalls.
3. Reduces Waste, Saves Money
Because NDT doesn’t damage the part, every component that passes inspection can go on to be used, unlike destructive testing, which sacrifices every test sample. This can provide significant savings on material costs. Additionally, with NDT, you can test a greater number of parts (or every part for that matter) for quality before deployment providing extra assurance in critical applications.
4. Supports Safety and Reliability
In industries like aerospace, automotive, defense, and energy, part failure isn’t an option. NDT ensures components are safe and reliable in critical applications.
5. Helps Meet Industry Standards
Many industries (ASME, ASTM, ISO, DoD, etc.) require NDT as part of their quality control and certification processes.
NDT Industry Applications:
Non-Destructive testing can be of a huge benefit to any company that values consistent, quality parts. It allows production teams to identify problems before parts go to market or into service.
Here are just a few examples of industries that commonly employ NDT:
- Nuclear Power
- Defense
- Oil & Gas
- Petrochemical
- Rail
- Aerospace
- Construction and Infrastructure
Conclusion:
Non-destructive testing is a powerful addition to QC efforts! We've explored several NDT methods, including penetrative testing, magnetic testing, visual testing, and X-ray. We've also touched on the benefits of NDT and industries that commonly use it during manufacturing.
At IPC, we proudly offer NDT services alongside our full suite of metalworking services (investment casting, machining, and rapid prototyping). With over 45 years of experience producing quality metal components, IPC is a production partner you can count on, whatever the scope or scale of your project. Need help with NDT or want to save time, money, and headaches on your next casting project?